Micro etching is an accurate manufacturing process that creates complex patterns on metal sheets. During micro etching, a controlled, uniform chemical reaction occurs that removes material at a microscopic level. Micro etching can be used on components that need very fine tolerances and complex feature designs. These components are used in many industries, including electronics, aerospace, and medical. Micro etching can be applied to delicate materials and complex shapes.
This article discusses what micro etching is, how it works, what it is used for, and the advantages of micro etching.

What is Micro Etching?
Micro etching is a chemical process that removes materials from metal surfaces. This technique can produce extremely detailed and precise features and patterns. Micro etching utilizes chemical solutions to selectively soak up the unwanted areas of the metal, while protecting the desired area during the etching process.
Micro etching works at the micrometer level to create tolerances and details that would not be attainable with mechanical processes. Micro-etching can be performed on various metals, which include:
- Stainless steel
- Copper
- Aluminum
- Titanium, and more.
Micro-etching can generate features that are a few microns in size with low percent material waste.
The Micro Etching Process
- The process begins with cleaning the sheet metal of any oils or contaminants. A photosensitive coating is then applied to both sides of the sheet metal. The photosensitive coating acts as a protective coating during the etching process.
- Next, the film with the desired pattern is placed. The pattern is exposed to UV light through the films. Once the photosensitive coating is exposed, it becomes soluble and is washed off, leaving the exposed metal at specific spots.
- Finally, the exposed metal receives a spray of chemical etchant (such as ferric chloride), which dissolves the exposed metal, while the photosensitive coating protects the covered area of the metal. The etching continues until the chosen depth of material has been removed.
Applications of Micro Etching
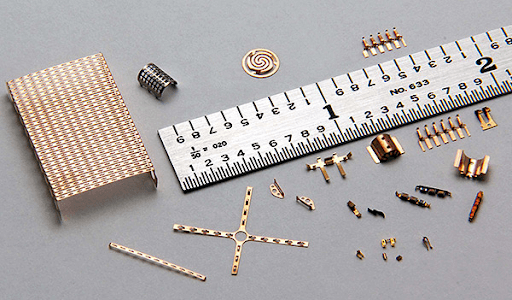
Electronics
Micro etching is used to remove unwanted copper from laminated boards, creating conductive pathways. Additionally, manufacturers create shielding components and connectors using micro etching. Mobile phones and computer components contain micro-etched components, as this it allows for miniaturization without damaging sensitive substrates.
Medical Devices
In medical applications, materials are required to be biocompatible and burr-free. Micro etching is used to produce medical components using titanium, nitinol, or other alloys. The micro etching process does not cause any mechanical stress, which is critical for implantable devices. Stents with micropores can be microetched to control medication release.
Common medical components include:
- Surgical scalpels and blades
- Vascular stents
- Catheter components
- Diagnostic sensors

Aerospace
The aerospace industry requires components that are lightweight yet durable. Micro etching can create parts for fuel systems, including filters and injector plates, where reducing weight is essential. Micro etching is used to produce encoder disks and heat exchangers with very intricate patterns of channels. Aerospace components must perform while exposed to extreme conditions, and micro etching preserves the material properties and does not introduce heat distortion.
Automotive
Micro etching can be found in the automotive manufacturing sector for fuel injection components and the housings for sensors. The components used in electric vehicle batteries withstand the etching process. Micro etching is useful for very thin materials, as the process does not warp materials.
Advantages of Micro Etching
Micro etching is used in precision manufacturing due to its multiple advantages:
Precision
Micro etching can achieve tolerances down to a few microns that are unattainable without mechanical processes. It can replicate complex geometries with complex patterns, as the design is transferred directly from photographic film to metal.
No Mechanical Stress
This process does not use any contact or heat. Hence, the parts will not have burrs, warping, or dimensional changes to the part. Materials will retain their original mechanical properties. This is critical for components that are required to have specific performance requirements.
Material Flexibility
Multiple metals, ranging from stainless steel to copper to aluminum and titanium, can be processed via appropriate chemical etchants. Thin materials, which can deform, by cutting tool or drill pressure, can be etched without issues.
Cost-Effective Production
Micro etching usually uses photographic film instead of costly dies/molds for tooling. Only photographic films are necessary for potential design changes in the component, which reduces costs and cycle time for design changes. This is what makes the micro etching process reasonable for prototyping or small production runs. In addition, the same process can scale up to large quantities without any highly significant equpiment changes.
Micro Etching vs Photochemical Etching
Although micro etching and photochemical etching are both precision processes, they serve very different purposes. Micro etching is concerned with changing a surface at the microscopic level to improve functional characteristics. Photochemical etching is about shaping metal with photolithographic precision.
- Micro etching changes surface texture without penetrating the material.
- Photochemical etching removes material completely to create complex patterns or parts.
- Micro etching enhances adherence, bonding, or optical behavior.
- Photochemical etching creates complex geometries and tolerances.
TMNetch Precision Photo Chemical Etching
TMNetch is a photochemical etching company that integrates scale, precision, and material versatility. They have a total workflow management system, from material selection all the way through to finishing & inspection. Here’s what makes them different:
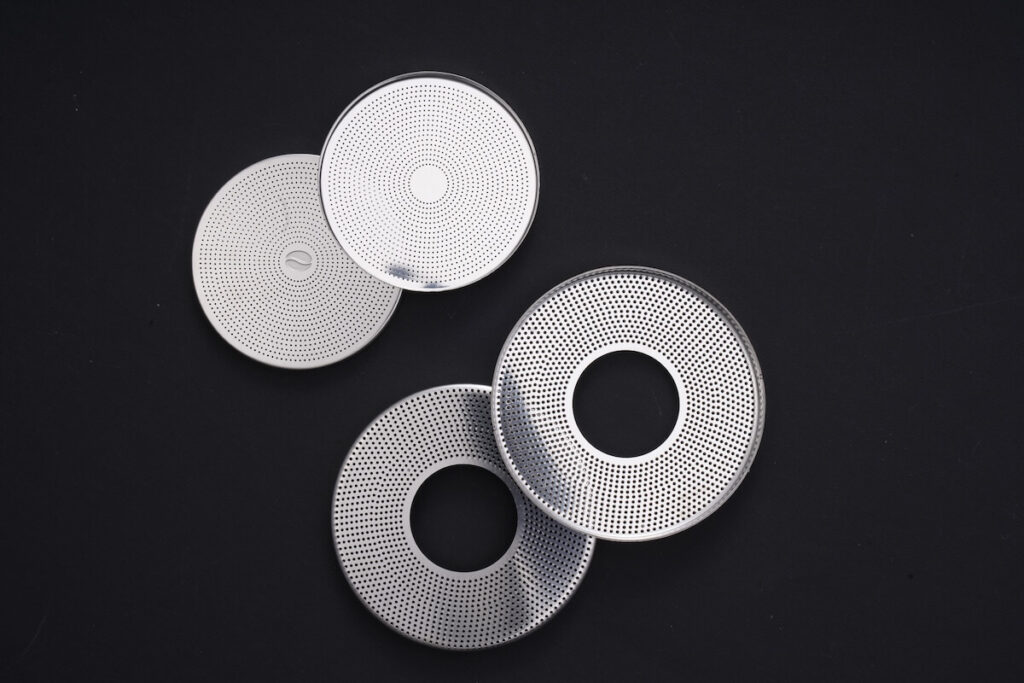

- They can process metal thicknesses from as low as 0.01 mm up through 2.5 mm (for most alloys).
- TMNetch keeps a wide range of metals in stock, including stainless steels, aluminum alloys, copper/brass, nickel, and titanium variations to offer a variety of metal characteristics.
- They can achieve ultra-thin etching down to 0.02 mm thickness and maintain the dimensional spot-on.
- They process over 1800 square meters of metal each day, all while keeping ISO 9001:2015 standards.
Contact TMNetch to discuss your custom project.
FAQs About Micro Etching
What is micro etching in dentistry?
Micro etching in dentistry uses fine abrasive particles and/or milder acidic etching agents for a micro-cosmic roughening of metals and ceramics. The result of the micro etching process is a roughened surface that aids in the mechanical retention of dental cements or veneers to the restoration.
What is the difference between micro etching and macro etching?
The micro etch is aimed a treating the microscopic surface layer of the surface in service, carefully exposing, or treating small features, some of which may relate to adhesion. The macro etch is used for much larger features and generally to reveal grain structures, or welds, or a large flow pattern visible to the naked eye.
What are common etching mistakes?
Common mistakes consist of over-etching, contamination, or failing to clean the surface adequately before treating. Others may not achieve proper chemical strength concentration or have time and temperature controls, all resulting in unreliable, inconsistent results, or lost adhesion or surface damage.
Conclusion
With industries requesting smaller and more precise parts, micro etching is gaining importance. Micro etching enables intricate designs without harming the materials, and it fosters advancements in many different areas. New technologies will help keep micro etching at the forefront of technology, as the need for precise and reliable components will not go away.
