Using inappropriate photochemical etching materials can bend, break, and ruin the parts. Sometimes, you choose the material randomly without studying its specifications and properties. Every material has its own structural composition, stability, and hardness.
Choosing the material that is not capable of photochemical etching can waste time, money, and effort. Poor metals can corrode, warp, or fail under heat, making your project a nightmare. That’s why using the right material is critical.
Read the guide to study different types of photochemical etching materials, their composition, and the best applications. So, you pick the one for your next etching project.
Why Does the Selection of the Right Photochemical Etching Materials Matter?
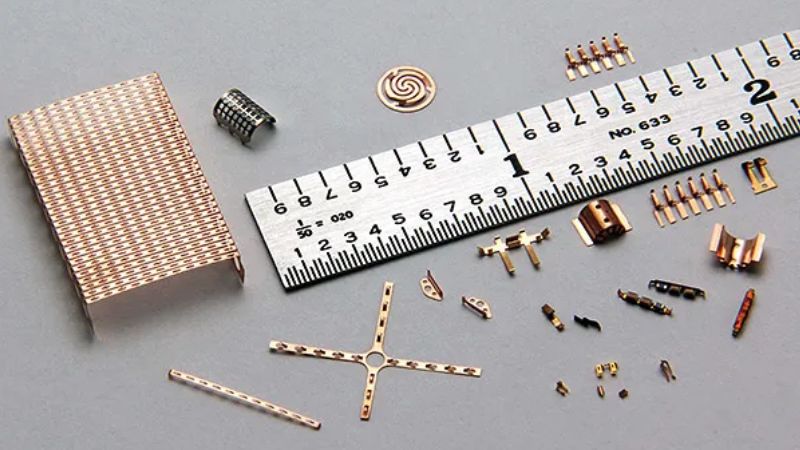
Photochemical etching process results depend on the nature, composition, and properties of metasils. The material that is unsuitable for anything not only consumes your time but also wastes your expensive metals. So, the selection of the right material matters a lot. Here are the three reasons you should pay attention to the selection of the best materials for photochemical etching.
Reason 1: Precision and Accuracy in Etching
The right material allows etching at fine tolerances. Metals like brass or stainless steel react predictably to chemical etchants. This ensures sharp edges and clean patterns. Inappropriate metals may over-etch and make the edges rough. The proper selection saves you from rework and starting a new project easily.
Reason 2: Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Some metals corrode easily in mild chemical exposure. Make sure to use corrosion-resistant photochemical etching materials like nickel alloys, titanium, or Inconel. These metals perform well in harsh environments where they face moisture, heat, or chemicals. Furthermore, ensure the material is durable and requires less maintenance.
Reason 3: Cost Efficiency and Production Speed
The selection of material for etching also impacts cost and speed. Make sure to use the metals that etch predictably, which reduces wasted material and labor if you choose the right material. It speeds up production and lowers overall expenses.
Key Materials Used in Photochemical Etching
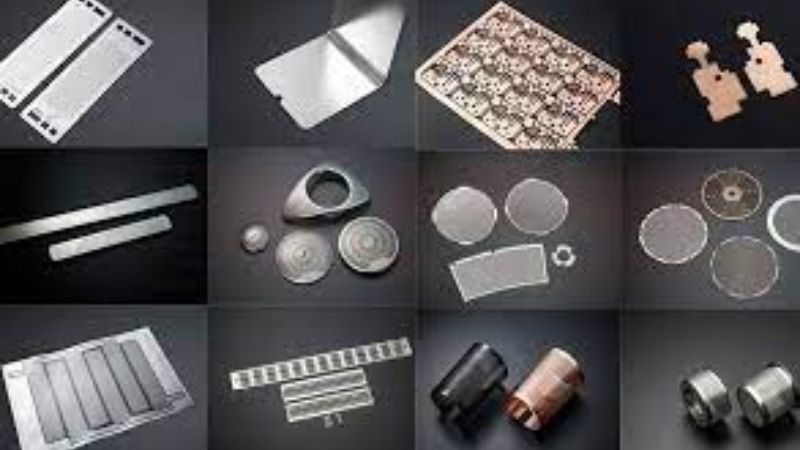

Photochemical etching works best when the right material is selected. The different metals react differently to etchants. So, selecting the right type ensures precision, durability, and reliability. Below is a detailed overview of photochemical machining materials.
Common Materials
The common metals are used widely in every industry and are cost-effective. The common photochemical etching materials include.
- Brass – Copper-Zinc alloy (Cu 60–70%, Zn 30–40%)
- Stainless Steel – Mostly Fe, with 10–20% Cr, small amounts of Ni and Mn
- Copper – Cu ≥ 99%
- Aluminum – Al ≥ 99%, sometimes alloyed with Mg or Si
Specialized Materials
These metals are high in demand for their superior performance. The specialized types of metals used in photochemical etching include
- Nickel and Nickel Alloys – Ni ≥ 60%, with Cr, Mo, Fe
- Titanium – Ti ≥ 99%
- Molybdenum – Mo ≥ 99%
- Inconel – Ni 50–70%, Cr 14–21%, Fe balance
Emerging & Advanced Materials
These materials are best suited for delivering micro-scale production in photochemical etching.
- Nanostructured Metals: Different metals combine at the nanoscale
- Eco-friendly Alloys: Recyclable metals
- Hybrid Laminates: Layers of different metals
Comparison of Photochemical Etching Materials Specifications
| Material | Etching Precision Potential | Corrosion Resistance | Thermal Stability | Cost Considerations | Best-Fit Applications |
| Brass (Cu 60–70%, Zn 30–40%) | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Decorative parts, nameplates, and connectors |
| Aluminum (Al ≥99%) | Moderate | Good | Moderate | Low | Aerospace, automotive, lightweight components |
| Stainless Steel (Fe+Cr+Ni) | Moderate-High | Excellent | High | Moderate | Medical, industrial, food processing |
| Copper (Cu ≥99%) | Very High | Low-Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | PCBs, electronics, heat exchangers |
| Nickel & Nickel Alloys | High | Excellent | High | High | Aerospace, chemical industry, high-performance components |
| Titanium (Ti ≥99%) | High | Excellent | High | High | Medical devices, aerospace, chemical exposure |
| Molybdenum (Mo ≥99%) | High | Good | Very High | High | High-temp components, aerospace, electronics |
| Inconel (Ni 50–70%, Cr 14–21%) | High | Excellent | Extreme | Very High | Chemical plants, high-temp aerospace, turbines |
What Material Properties Should You Consider When Choosing for Photochemical Etching?
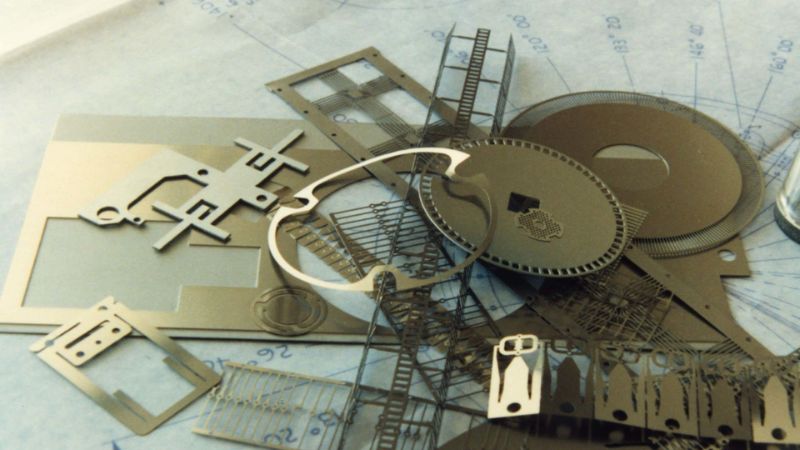
The selection of the best materials for photochemical etching is more than just picking a random metal and starting to etch. The metal properties directly affect etching quality, durability, and cost. Below are the key properties you should consider before making a final decision.
Alt Text: Material Properties in Photochemical Etching
Thickness Tolerances and Uniformity
You should consider the photochemical etching materials’ thickness and their consistency across the sheet. Uneven thickness can cause uneven etching. Choose the metals with tight thickness tolerances because they produce more accurate and repeatable patterns. The metal thickness is essential for electronics and precision instruments.
Grain Structure and Surface Finish
The metal with fine-grained etch etches more uniformly. Coarse grains can create rough edges or undercuts. Furthermore, the surface finish also matters to achieve cleaner chemical reactions. It’s important to select metals with the proper grain and finish for high-precision applications.
Chemical Compatibility with Etchants
Remember, not all metals react the same way with etchants. Some metals rust fast and over-etch within a few minutes. On the other hand, some metals may under-etch or corrode too fast. Checking the photochemical etching materials’ chemical compatibility ensures the metal will etch predictably without damaging the part.
Thermal Expansion Behavior
Generally, metals have a nature to expand and contract with heat. Materials with high thermal expansion can warp during etching or heat exposure. Choose the metal with stable thermal properties that ensures dimensional accuracy.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
High-volume production industries often select metals that meet industrial standards. Materials may need to meet RoHS, REACH, or ISO standards. Furthermore, they prefer environmentally friendly alloys that reduce waste and chemical hazards. Compliance ensures safety and avoids costly recalls or fines.
TMNetch—Best Supplier to Meet Your Photochemical Etching Materials Needs
TMNetch is a leading supplier of photochemical etching materials and services. They provide a wide range of metals. It includes brass, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, nickel alloys, titanium, and hybrid laminates. Each material is carefully sourced and certified, ensuring reliability.
The brand offers a full spectrum of photochemical etching process services. From prototyping to pilot runs, they handle every stage with precision. Their processes allow micron-level accuracy and make complex designs without compromising quality.

They collaborate closely with your engineering teams and support design-for-manufacturing (DFM) adjustments till final inspections. So, they make sure to ensure each part meets exact specifications. This technical support for large-scale production reduces costly errors.
One of the key strengths of this company is its commitment to quality and precision. Strictly following industry compliance and safety standards makes them stand out. TMNetch also helps clients ensure safe photochemical etching material usage and etching production efficiency.
FAQs
What chemicals are used in chemical etching?
The chemical etching process uses strong acids and solutions to remove metal parts. Ferric chloride is a common chemical used in etching. You can also use copper and brass, nitric acid for stainless steel, and sodium hydroxide for aluminum. These chemicals eat away at metal where needed. Make sure to wear safety gear to prevent accidents and damage.
Which acid is used in etching?
The acids used in etching depend on the nature of the metal. The acid etching commonly uses hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. These acids remove metal where needed. However, the chemical reaction of this acid is too fast and may burn your hands. So, make sure to wear gloves to handle this reaction.
How many types of etching are there?
Dry and wet etching are two common types of chemical etching. In wet etching, you commonly use liquid chemicals to remove metal. Dry etching uses gases or plasma to cut metal. Each type works differently and is chosen based on the metal and design.
Final Thoughts
To sum up, the photochemical etching materials are a key factor in achieving precise photochemical etching results. However, how to choose materials for photochemical etching is a matter. The selection of a suitable material ensures your design etches cleanly and performs as intended. Using unsuitable metal leads to poor etch quality and makes the surface uneven. You must check the photochemical etching materials specifications, certifications, and compatibility with your etching process before starting. Always source materials from trusted suppliers to avoid defects. Make sure to test a small material sample first and check the reaction in response to etching. A suitable photochemical etching material helps maintain micron-level precision and consistent production quality.
