The chemical etching works under controlled chemical reactions to remove metal in exact patterns. Generally, the engineers use etching to remove metal parts. They also employ this process to produce intricate designs without mechanical stress, heat distortion, or burr formation. However, the chemical etching applications are not limited to making designs in metal surfaces.
The aerospace manufacturers also use it to create turbine shims and precision fuel filters.
On the other hand, the electronics and semiconductor industries use it for EMI/RFI shielding. The chemical etching uses a different range of materials, like stainless steel, copper, and brass.
This is the main reason each sector prefers this process to other traditional methods. Read the guide to explore the chemical etching applications across various industries.
Chemical Etching Applications: Where Can This Technology Deliver the Most Impact?

Generally, chemical etching is used to shape the thin metal sheet without distortion. However, many industries adopt this technology to achieve excellence in their fields. Here is a detailed overview of the application and benefits of chemical etching in manufacturing.
Aerospace Applications
In the aerospace chemical etching applications, every gram counts and every tolerance matters. Chemical etching is ideal because it removes metal evenly and keeps dimensions accurate. It is also scalable for small or large production runs without buying expensive tools. Here is how chemical etching is used in aerospace to make:
- Turbine shims
- Fuel filters
- Satellite antenna meshes
The turbine shims are thin spacers that keep the turbine blades in exact position. You can also design fuel filters with a mesh that can have hole sizes. This ensures clean fuel delivery without risk of particle contamination. Etching also designs the communication satellite meshes that transmit signals at specific frequencies.
Medical Device Applications
Medical parts need to be reliable, sterile, and dimensionally precise. Chemical etching achieves these needs without introducing heat. It can also produce ultra-fine features that are impossible with mechanical cutting. You can make:
- Surgical blades
- Stents
- Microfluidic channels
Etching designs the blades that provide extreme sharpness. This improves surgical accuracy and reduces patient recovery time. You can also make a channel to control the levels of blood flow rate. Furthermore, etching also enables you to create thin tubes with uniform stents.
Electronics & Semiconductor Applications
The electronics industry requires thin, conductive, and intricately patterned metal parts. Etching works well because it can cut micron-scale details. Here are the following applications of chemical etching in electronics:
- EMI/RFI shields
- Flex circuits
- Photomasks
The EMI etched shields block the harmful frequencies. You can use this process in devices like a camera and a smartphone. Etching patterns the coppertraces with precision and ensures current flows evenly. In semiconductor production, etching produces crisp, defect-free openings in the mask.
Automotive Applications

Automotive vehicles demand durable parts that maintain performance under vibration and high-volume production. Chemical etching in this industry offers repeatability and fine detail. Here, chemical etching for metal fabrication is used to make:
- Injector filters
- Precision washers
- Heat exchanger plates
In modern engines, the injector filters are used to prevent the injector from clogging. Etched filters are also designed to ensure the even distribution of fuel. Furthermore, you can make washers from the etching process to reduce the wear in machinery.
Industrial Equipment Applications

Many manufacturing systems need parts that fit exactly and operate reliably under continuous use. Etching provides fast production of custom designs without tooling delays. So, your machinery remains durable and performs for a long time. You can make the following equipment by using chemical etching for micro-machining:
- Sieves
- Shims
- Precision spacers
The sieves are used for sorting powders or liquids. The etched sieves have exact hole sizes for consistent product quality. On the other hand, the shims are
used for machine alignments. This allows precise adjustment without the need for grinding.
Decorative & Architectural Applications
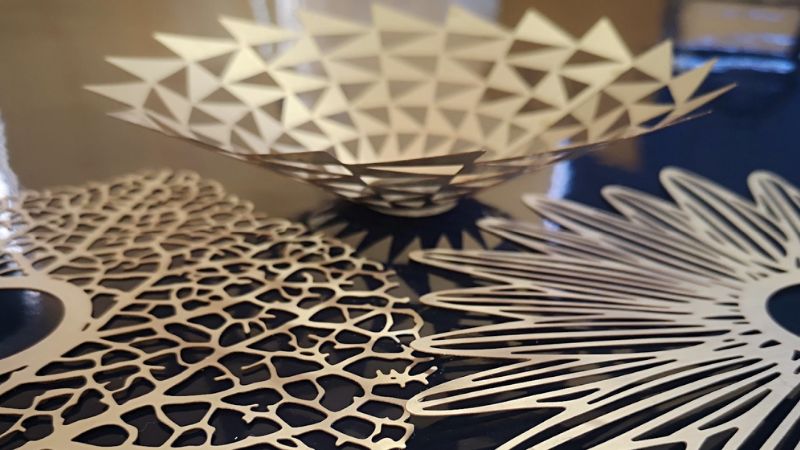

Etching is also used for high-end visual designs in metals. It enables patterns and text to be created with unmatched detail. In the architectural field, you can employ chemical etching to make:
- Nameplates
- Luxury panels
- Intricate facades
Most company branding, serial numbers, or safety instructions use nameplates. They design these plates using a chemical etching process. The high-end cars, yachts, and interiors use etched panels for custom finishes. The process can combine fine textures with precise cutouts.
Energy & Renewable Sector Applications
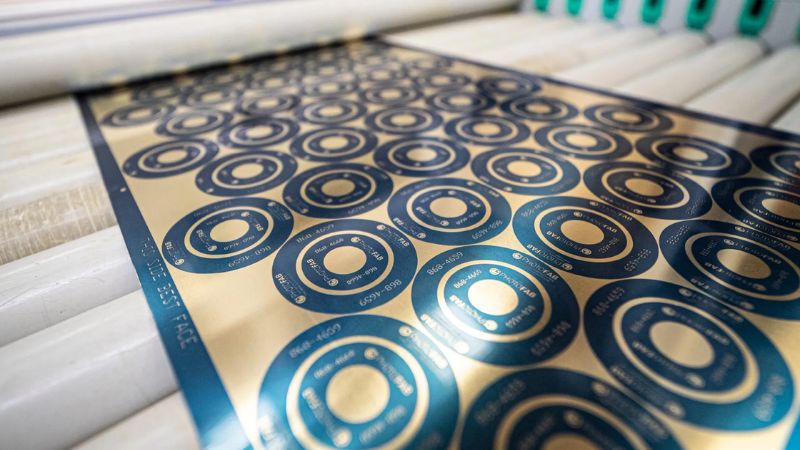

Energy systems demand efficiency, corrosion resistance, and lightweight construction. Etching meets these requirements. This process allows advanced fluid and electrical designs. The engineers in this industry use etching to make:
- Fuel cell plates
- Wind turbine components
- Solar panel connectors
The fuel cell plates contain etched channels that guide hydrogen and oxygen gases through the cell. The solar panel connectors reduce electrical resistance. The etching process optimizes the panel shapes for quick installation and minimal shading.
Why Industries Prefer Chemical Etching Over Other Manufacturing Methods
Chemical etching is 180 degrees different from cutting, stamping, or laser work. It uses controlled chemical reactions to remove metal. The process works without heat. Here are a few reasons why industries prefer this process.
Precision Without Physical Stress
In mechanical cutting, heat can change the shape of thin metals. This can cause warping or micro-cracks. Chemical etching removes metal without touching the part. There is no pressure, which means no distortion. The result is exact dimensions with the metal’s original strength intact.
Complexity at No Extra Tooling Cost
With stamping, complex shapes need new tools. This adds cost and time. In chemical etching, the “tool” is a photographic mask. To make a new design, you only change the mask pattern. This allows intricate shapes and fine details without buying hard tooling.
Consistency and Repeatability
In chemical etching, the process is controlled by certain times, temperatures, and chemical mixes. These can be held steady over long runs. This means the first part and the last part have the same shape and thickness. It eliminates the chances of changing the material thickness at the end.
Wide Material Compatibility
Traditional cutting methods struggle with hard alloys. Chemical etching can work with stainless steel, copper, brass, nickel, titanium, and more. Even very hard materials can be processed without cracks. This ensures clean removal without attacking protected areas. TMNetch has the capability to work with many different materials while maintaining high precision and quality.
Burr-Free, Clean Edges for Critical Applications
The chemical etching dissolves metal parts evenly. This leaves edges smooth and free of burrs. It means better performance and no need for extra deburring steps. You can work on large production without worrying about bubbles and burrs at the end.
TMNetch—Photochemical Etching Specialists in Metal Component Production

TMNetch is a well-known supplier that delivers photochemical etching services across various industries. They produce precise metal components without breaking the bank. The company focuses on achieving high accuracy and keeping the integrity of each material intact.
They are known for their material-specific etching expertise. Brass, stainless steel, and copper each respond differently to chemicals. TMNetch understands these differences. Their engineers adjust and monitor the temperature and masking techniques during etching. This ensures exact tolerances and clean finishes without heating the metal.
Their engineers get in touch with clients to review and refine designs before production. They observe tolerances and feature sizes to make sure the part will etch correctly.
TMNetch customer support is responsive and easy to reach, helping clients at every step. Many clients share positive feedback, noting the clear communication and reliable guidance they receive.
Alt Text: TMNetch—Photochemical Etching Specialists
Here is the detail about the brand’s material handling process along with their specifications.
| Material | Etching Precision Range | Typical Thickness Range | Surface Finish Quality | Key Applications |
| Brass | ±0.025 mm | 0.05 – 1.5 mm | Smooth, bright | Decorative panels, electrical connectors, gears |
| Stainless Steel | ±0.025 mm | 0.025 – 1.2 mm | Clean, corrosion-resistant | Filters, medical tools, aerospace parts |
| Copper | ±0.020 mm | 0.025 – 1.0 mm | High conductivity, clean edges | PCB parts, EMI/RFI shielding, fine electrical parts |
FAQs
How many types of etching are there?
There are two main types of etching: dry etching and wet etching. The wet etching uses liquid chemicals to remove metal. On the other hand, dry etching uses gases. Both can produce fine detail. However, the method depends on the design requirements.
What is the principle of etching?
The basic principle of etching is removing material from a surface. This process mostly uses chemicals and gases. A mask protects certain areas. While the exposed parts react, this controlled removal creates patterns without affecting the metal’s structure.
What is the difference between AC and DC etching?
The AC etching uses alternating current and gives a cleaner surface with less burr and oxidation. On the other hand, the DC etching uses direct current, which gives deeper, faster cuts. The selection of one among them depends on material behavior.
Final Thoughts
To sum up, the chemical etching applications cover a wide range of industries. From aerospace and automotive to electronics and medical devices, the etching provides quality results. The process allows engineers to create complex shapes. It works on many materials, such as stainless steel, copper, and brass.
However, the chemical etching application process demands care. A small error in timing, temperature, or chemical strength can ruin the pattern or damage the part.
Following the correct steps, using the right tools, and wearing proper safety gear. So, it is best to follow safety rules and proven techniques to make sure your project is accurate and safe.
